Search Results for: suffix
Isomaltose
Definition noun plural: isomaltoses i·so·mal·tose, aɪsoʊˈmɔːltəʊz A disaccharide formed from the combination of... Read More
Aneuploidy
Definition noun (genetics) The chromosomal variation due to a loss or a gain of one or more chromosomes resulting in the... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
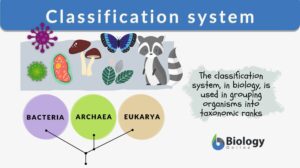
Classification system
Classification Systems Definition In life, many things are classified, that is, to put into categories or groups based on... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
Deoxyribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: deoxyribonucleotides de·ox·y·ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, diˌɒk... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Oligonucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides ol·i·go·nu·cle·o·tide, ŏl′ĭ-gō-no͞o′klē-ə-tīd A short polymer... Read More
Dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: dinucleotides di·nu·cle·o·tide, daɪ njuːklɪəˌtaɪd An organic compound comprised of two... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
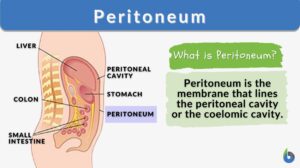
Peritoneum
What is the Peritoneum? The term peritoneum refers to the serous membrane that constitutes the biologically active inner... Read More
Complement
Complement (Science: immunology) a term originally used to refer to the heat labile factor in serum that causes immune... Read More
Mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A single nucleotide (as... Read More