Search Results for: toxic
Obligate aerobe
Before we define obligate aerobes, let us first understand and define aerobic organisms. Aerobic organisms are those that... Read More
Dead Man Walking
Dead Man Walking: Wade Davis and the Secret of the Zombie Poison By Patrick D. Hahn Accepted on September 4, 2007 Twenty... Read More
Commensalism
Commensalism Definition What is commensalism? Literally, commensalism is a Latin word that means ‘to eat at the same... Read More
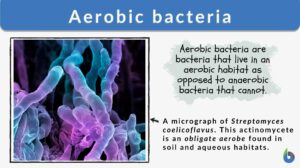
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
Biological magnification
Definition noun, plural: biological magnification The increasing concentration of a particular substance (e.g. toxin) as it... Read More
Industrial Microbiology
Definition noun Related to environmental, social and economic importance that are engaged in the utilization of... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Hexosaminidase A
Definition noun A hydrolytic enzyme implicated in the breakdown of ganglioside producing... Read More
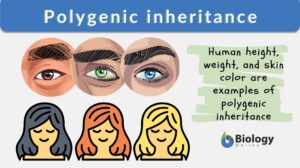
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Pollution in Freshwater Ecosystems
As with all ecosystems, the existence and operations of human society inevitably have an effect on the way of life in a... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Environmental resistance
Environmental Resistance Definition Environmental resistance is such a process in which certain different elements or... Read More
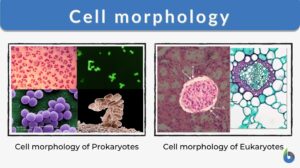
Cell morphology
The basic essence for any living organism is its structural framework which includes appearance, form, and the... Read More
Nasogastric aspiration
Definition noun An aspiration technique in which the gastric contents are removed or drained using a nasogastric tube that... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Streptolysin S
Definition noun A nonantigenic, oxygen-stable β-hemolytic enzyme produced by some bacteria, especially... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Dohle body
Definition noun, plural: Dohle bodies Round or oval cytoplasmic inclusion of neutrophils containing remnants of rough... Read More
Millons test
Definition noun A color reaction test using Millon's reagent to detect phenolic compounds (e.g. tyrosine) Supplement French... Read More
The consequences of antibiotic use in horticulture
Leading articles Frederick R. Falkiner* Department of Clinical Microbiology, Trinity College, Dublin; Central Pathology... Read More
Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
Darwin focused some of this work in regards to the population size of a species, and what factors may affect them. He... Read More
Growth and Development of a Human Baby
Continued from the initial human reproduction of the previous page in this tutorial. Upon arrival in the uterus, the... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Mucolipidosis
Definition noun A type of mucopolysaccharides and mucolipids Supplement Lysosomal storage disease is a collective term for... Read More
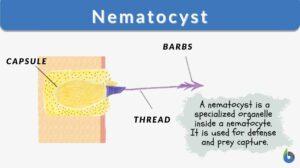
Nematocyst
All organisms are composed of millions of cells. Many cells serve specific purposes and are specialized to do distinct... Read More
Austin disease
Definition noun A type of lysosomal storage disease that is often caused by a deficiency in multiple sulfatase enzymes, or... Read More