Search Results for: tubular
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
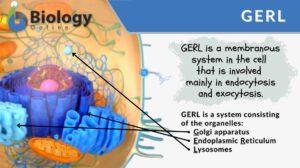
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
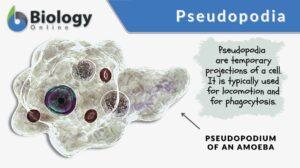
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Angiotensinogen
Definition noun An alpha-2 globulin protein that is found in the bloodstream and release into circulation mainly by the... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Muscle cell
Definition noun, plural: muscle cells Any of the long, tubular mature contractile cells that make up the muscle... Read More
Microtubule
Microtubule Definition noun plural: microtubules mi·cro·tu·bule, mī'krō-tū'byūl A cytoplasmic tubule made up of... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Hyposmotic
Definition adjective 1. Of, relating to, or characterized by having a lower osmotic pressure than a surrounding fluid under... Read More
Tracheary elements
Definition noun (botany) The principal conductive cells of the xylem associated with the conduction of water and minerals... Read More
Microfibril
Definition noun, plural: microfibrils (1) (cell biology) A microtubule or microfilament within the cell; an extremely small,... Read More
Microtubule organizing center
Definition noun A structure inside the cell from where microtubules organize following depolymerization to turn into tubular... Read More
Adaptive radiation
Definition noun The diversification of several new species from a recent ancestral source, each adapted to utilize or... Read More
Stratified columnar epithelium
A stratified columnar epithelium (plural: stratified columnar epithelia) is a type of stratified epithelium in which the... Read More
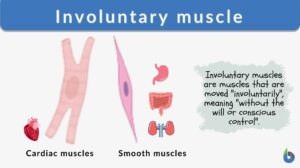
Involuntary muscle
A muscle act typically either under the control of the will or without conscious control. Muscles that can be controlled at... Read More
Chromoplast
Definition noun, plural: chromoplasts Any of the coloured plastids associated with pigment synthesis and... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Foveolar cell
Definition noun, plural: foveolar cells Any of the epithelial cells that line the surface of gastric mucosa and gastric... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More



![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)