Search Results for: two-step
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
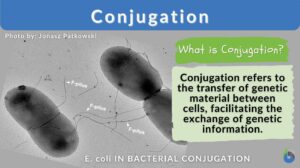
Conjugation
Conjugation generally means the joining or coming together (union), such as in certain unicellular organisms (some bacteria,... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Allopatric speciation
We can define speciation as a process by which the novel genetically independent group of organisms are formed through the... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction involving the fusion of haploid female gamete (egg cell) and haploid male... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Elongation
Definition noun (general) The state, act, or process of lengthening Supplement In general, the term elongation refers to the... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
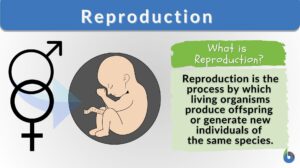
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
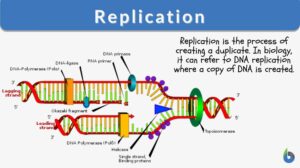
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Termination
Definition noun (general) The process, act, or state of terminating (biochemistry) A process in which the mRNA synthesis... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Initiation
Definition noun (general) The beginning of a state or of a process; the act of initiating Supplement In general sense, the... Read More
Using Antibodies : A Laboratory Manual : Portable Protocol NO. I
Using Antibodies : A Laboratory Manual : Portable Protocol NO. I ... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More