Search Results for: aids
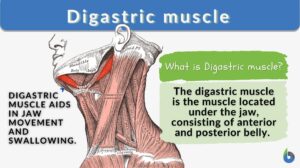
Digastric muscle
Digastric Definition The digastric muscle is a paired muscle located under the jaw, consisting of the anterior and... Read More
Imprinting
What does imprinting mean? Have you watched the TV cartoon show “Tom and Jerry” with an episode of a duck and its... Read More
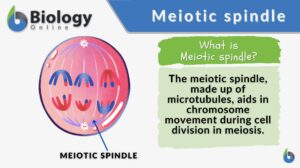
Meiotic spindle
Meiotic Spindle Definition The meiotic spindle refers to the spindle apparatus that forms during meiosis in contrast to... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Hypomelanism
All the body cells of living organisms bear some color due to one or the other pigment molecule or complex. The pigment can... Read More
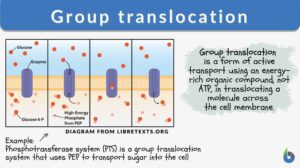
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
Thalassophobia
Among many psychological and psychiatric disorders, one is the fear of the ocean and the fear of deep water, which in... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Pioneer species
You might have come across news of some barren lands turning into luscious grasslands or forests after decades? Or you might... Read More
Parietal cell
Definition noun, plural: parietal cells Any of the epithelial cells in the gastric gland responsible for the secretion of... Read More
Sexually transmitted disease
Definition noun, plural: sexually transmitted diseases (pathology) A disease that is primarily contracted through sexual... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Gastric juice
Definition noun The acidic digestive fluid secreted by various glands in the stomach lining into the lumen of the stomach,... Read More
Genetic variability
Genetic Variability Definition Genetic variability refers to the tendency of individual genetic characteristics in a... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Isomaltose
Definition noun plural: isomaltoses i·so·mal·tose, aɪsoʊˈmɔːltəʊz A disaccharide formed from the combination of... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
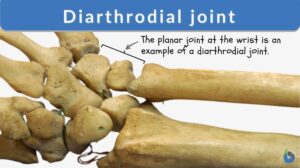
Diarthrodial joint
What is a diarthrodial joint? A diarthrosis joint is a freely moving joint characterized by its mobility and joint cavity... Read More
Transcellular fluid
Definition noun A bodily fluid found in chambers created by the linings of epithelial cells Supplement The extracellular... Read More
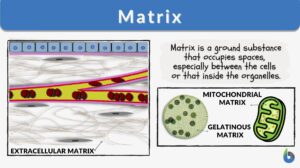
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Thermophile
Thermophiles Definition What are thermophiles? Let us first understand the literal meaning of the word ‘thermophile’.... Read More
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia Definition Each person can say that they know of or can name at least one animal. However, do people know... Read More