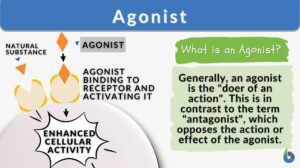
Search Results for: bind
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Definition noun plural: sarcoplasmic reticula (cell biology) The special type of smooth endoplasmic reticulum found in... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Competitive binding assay
Definition An assay based on the competition between labeled and unlabeled ligand for the reactive sites of a particular... Read More
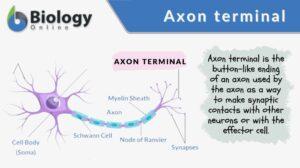
Axon terminal
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
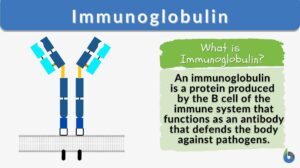
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
Oligonucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides ol·i·go·nu·cle·o·tide, ŏl′ĭ-gō-no͞o′klē-ə-tīd A short polymer... Read More
Repressor protein
Definition noun, plural: repressor proteins A protein in which its binding to the operator inhibits the transcription of one... Read More
Opsonization
Definition noun, plural: opsonizations The process at which opsonins bind to the surface of the antigen so that the... Read More
Hemoglobin
Definition noun, plural: hemoglobins A biomolecule made up of haeme (i.e. oxygen-carrying, nonprotein, ferrous component)... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Plasmablast
Definition noun, plural: plasmablasts An antibody-producing stem cell that could give rise to another of its kind or... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Single-stranded DNA
What is single-stranded DNA? DNA is the material that living organisms possess that carries their genetic make-up. DNA and... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Oxyhemoglobin
Definition noun, plural: oxyhemoglobins A bright red hemoglobin carrying oxygen molecule Supplement One of the main... Read More
Substrate specificity
Definition noun A feature of enzyme activity with regard to the kind of substrate reacting with an enzyme to yield a... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
Promoter gene
Definition noun, plural: promoter genes (genetics) A site in a DNA molecule at which RNA polymerase and transcription... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
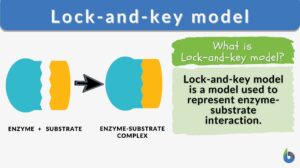
Lock-and-key model
Lock-and-key model Definition Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and... Read More