Search Results for: building
RNA-DNA World Hypothesis?
How did life start as we know it? In the scientific community, the "RNA World Hypothesis" has many adherents. Many believed... Read More
Origins of Life on Earth
Although Earth was created around 4.5 billion years ago, life began to exist not long after. Due to the huge timescales... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
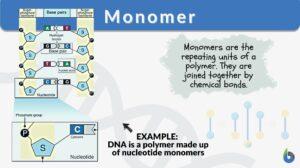
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Macrophytes
Introduction Examples of Macrophytes. (Source: Canada's AquaticEnvironments) ... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Alongside the numerous vitamins that are required as part of a healthy diet, we must also eat food containing a variety of... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
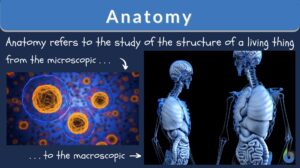
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
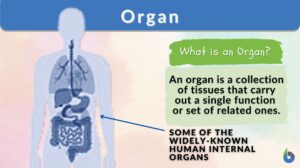
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia Definition Each person can say that they know of or can name at least one animal. However, do people know... Read More
Microscopic section
microscopic section --> section 1. The act of cutting, or separation by cutting; as, the section of bodies. 2. A part... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Deoxyribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: deoxyribonucleotides de·ox·y·ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, diˌɒk... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More