Search Results for: chamber
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Three-chambered heart
Three-chambered heart congenital abnormality in which there may be a single atrium with two ventricles or a single ventricle... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Goniosynechia
Definition noun, plural: goniosynechiae Synechia of the iris to the cornea in the angle of the anterior... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Vitreous humor
Definition noun The clear, gel-like body fluid in the vitreous chamber, i.e. the posterior cavity between the lens and the... Read More
Cardiovascular system
Definition noun The organ system in which the blood is pumped through the heart and circulates throughout the body through... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
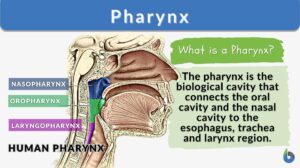
Nasopharynx
Definition noun, plural: nasopharynges or nasopharynxes (anatomy) The part of the pharynx extending from the posterior... Read More
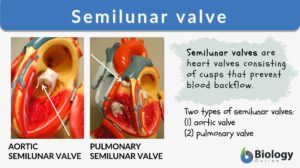
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
Absorption cell
Absorption cell a small glass chamber with parallel sides, in which absorption spectra of solutions can be... Read More
Sclerotome
Definition noun, plural: sclerotomes (embryology) The somite that gives rise to the development of vertebrae and... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Sense organ
Definition noun, plural: sense organs An organ or structure that has nerve endings capable of detecting and reacting to a... Read More
Sinus venosus
Definition noun In embryo, the cavity caudad of cardiac tube where the veins from the intra- and extraembryonic circulatory... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Aqueous humor
Definition noun, plural: aqueous humors A clear, watery body fluid secreted by the ciliary epithelium, and fills the... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More