Search Results for: diameter
Diameter obliqua
Diameter obliqua --> oblique diameter a measurement across the pelvic inlet from the sacroiliac joint of one side to the... Read More
Geometric mean diameter
Geometric mean diameter a measure of the central tendency of particle size composition of substrate materials sometimes used... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
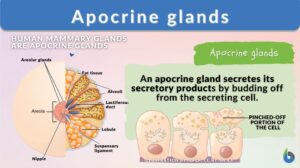
Apocrine gland
The human body is a complex assemblage of many different organs, systems, glands, bones, and tissues. Weighing any one over... Read More
Fahraeus-lindqvist effect
Fahraeus-lindqvist effect The decrease in apparent viscosity that occurs when a suspension, such as blood, is made to flow... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Thick filament
Definition noun, plural: thick filaments A type of myofilament that is made up of bipolar myosin II filaments, and is... Read More
Terminal hair
Definition noun The mature type of hair characterized by being pigmented, thicker, and with a larger diameter than the... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Myofilament
Definition noun, plural: myofilaments Any of the filaments made up of proteins and comprise the... Read More
Internal conjugate
Internal conjugate --> conjugate of pelvic inlet distance from the promontory of the sacrum to the upper posterior edge... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Nuclear body
Definition noun plural: nuclear bodies nu·cle·ar bod‧y, ˈnjuː.kli.ər ˈbɒdi Any of the prominent non-membraned,... Read More
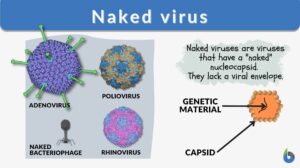
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Ascaris lumbricoides
Definition noun A parasitic roundworm of humans, generally dwelling in the intestines of human host Supplement Ascaris... Read More
Pinealocyte
Definition noun, plural: pinealocytes The major cell type component of the pineal gland, and is involved in the production... Read More
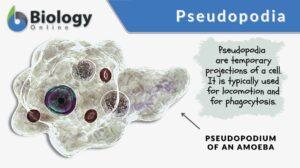
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Radial immunodiffusion
Definition noun A quantitative immunodiffusion technique used to detect the level of protein (antigen) in a sample by... Read More
Pollen Grain
What are Pollen Grains? Plants are unique structures and so they carry out mechanisms in special ways. Fertilization in... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Microtubule
Microtubule Definition noun plural: microtubules mi·cro·tu·bule, mī'krō-tū'byūl A cytoplasmic tubule made up of... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Blood Vessels Hold Key To Thicker Hair Growth
MGH researchers have succeeded in growing hair faster and thicker in mice, thanks to a protein that promotes blood vessel... Read More
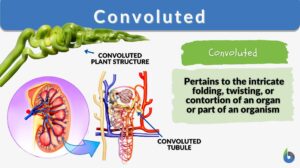
Convoluted
The word convoluted is often used to describe different things, especially structures or components, that have overlapped.... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Elastic fiber
Definition noun, plural: elastic fibers A type of connective tissue fiber that is made up, primarily, of elastin, and found... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More