Search Results for: differentiation
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Dedifferentiation
Definition noun (developmental biology) A cellular process in which a differentiated cell loses its special form or... Read More
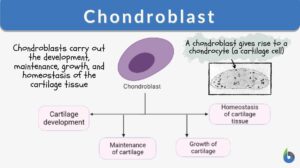
Chondroblast
There are two forms of cells in cartilage: chondroblasts and chondrocytes. The chondroblasts are cells that secrete the... Read More
Interspecific competition
Interspecific Competition Definition In Biology, competition is defined as the process that occurs among species that have... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Genetic variability
Genetic Variability Definition Genetic variability refers to the tendency of individual genetic characteristics in a... Read More
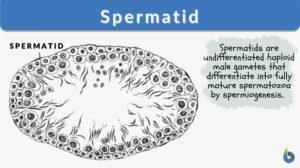
Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis Definition Spermiogenesis is the stage of spermatogenesis wherein the spermatids differentiate into mature... Read More
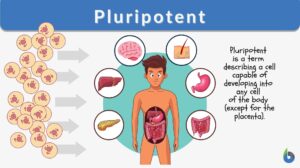
Pluripotent
Pluripotent Definition What is pluripotent? In biology, the term "pluripotent" means capable of developing into... Read More
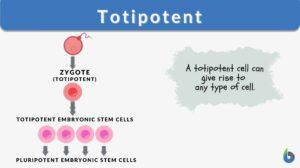
Totipotent
Totipotent Definition What is totipotent? In general terms, totipotency is defined as the ability of a single cell to... Read More
Maturation
Definition noun, plural: maturations (1) The process of differentiation (2) The process of becoming... Read More
Ecosystem diversity
Ecosystem Diversity Definition What is ecosystem diversity? Ecosystem diversity deals with the study of different... Read More
Myogenesis
Definition noun (embryology) The formation of muscle tissues through the differentiation of progenitor cells myoblasts... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Allotetraploid
Allotetraploid Definition An allotetraploid is an organism with four sets of chromosomes (4n). This is in contrast to the... Read More
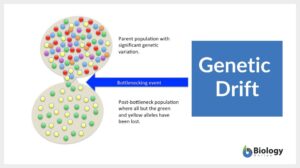
Genetic drift
Genetic Drift Definition What is genetic drift in simple terms? The simple definition of genetic drift ( also referred to... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Allopatric speciation
We can define speciation as a process by which the novel genetically independent group of organisms are formed through the... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More