Search Results for: directly
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
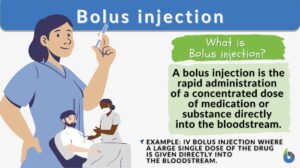
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Density dependent limiting factor
What Is A Density-Dependent Limiting Factor? Density-dependent limiting factors are limiting factors, which, depending on... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
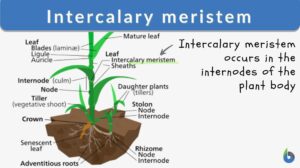
Intercalary meristem
The basic structural framework of plants is composed of different types of tissues. Based upon the capacity to divide, the... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
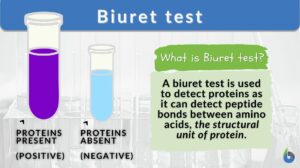
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
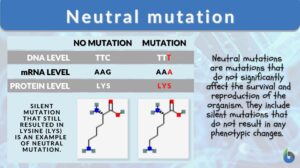
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
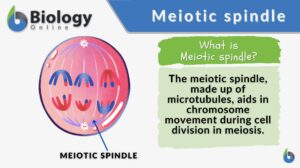
Meiotic spindle
Meiotic Spindle Definition The meiotic spindle refers to the spindle apparatus that forms during meiosis in contrast to... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
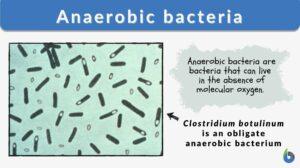
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
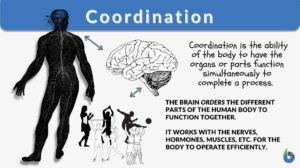
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
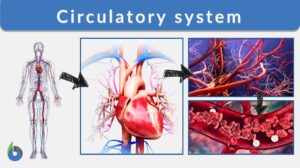
Circulatory system
Circulatory System Definition noun The organ system responsible for the circulation and transport of oxygen, carbon... Read More
Open circulatory system
Definition noun A type of circulatory system wherein the hemolymph bathes the organs and tissues directly thus there is no... Read More
Nasopharynx
Definition noun, plural: nasopharynges or nasopharynxes (anatomy) The part of the pharynx extending from the posterior... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
Online systems
online systems systems where the input data enter the computer directly from the point of origin (usually a terminal or... Read More
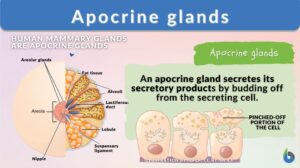
Apocrine gland
The human body is a complex assemblage of many different organs, systems, glands, bones, and tissues. Weighing any one over... Read More