Search Results for: gas
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
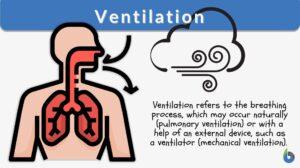
Ventilation
Ventilation Definition Often when persons think of ventilation, they think of getting clean or enough air into a room. This... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Greenhouse gas
Definition noun Any of the atmospheric gases responsible for the greenhouse effect. Supplement Examples of greenhouse gases... Read More
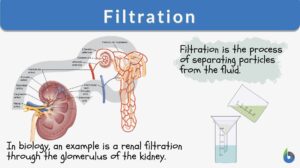
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
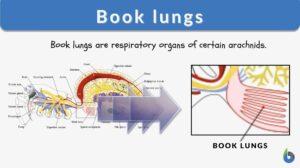
Book lungs
Book Lungs Definition Lungs are known as the organs that help organisms breathe. When we think of lungs, we think of the... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Respiratory system
Definition noun An organ system comprised of organs and structures associated for respiration or gas exchange Supplement An... Read More
Pneumatophore
Definition noun, plural: pneumatophores (botany) A specialized aerial root, such as in certain mangrove species, that stick... Read More
Nitrogen fixation
Definition noun The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a more usable form by natural means, such as by the... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Partial pressure
partial pressure The pressure exerted by a single component of a mixture of gases, commonly expressed in mm hg or torr; for... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Alveolar cell
Definition noun, plural: alveolar cells The cell lining the pulmonary alveolus; the cell of the air sac of the... Read More
Adsorption
Adsorption 1. (Science: chemistry) The accumulation or concentration of molecules of a gas or liquid on a surface in contact... Read More
Global warming
Definition' noun The recent increase in the Earth's average atmospheric temperature due to an increase in the levels of... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More