Search Results for: inverse
Proportion
proportion 1. The relation or adaptation of one portion to another, or to the whole, as respect magnitude, quantity, or... Read More
Density dependent factor
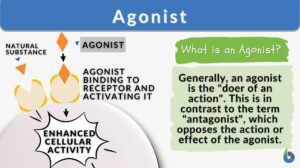
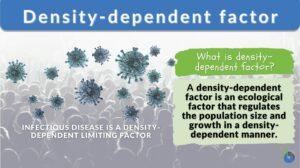
Density-dependent factors are the limiting factors of an ecosystem that regulate population growth in a density-dependent... Read More
Biomagnetism: Fundamental Research and Clinical Applications, (Studies in Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics , Vol 7)
Biomagnetism: Fundamental Research and Clinical Applications ... Read More
Overview of Chirology
Psychodiagnostic Chirology (PDC) is a comprehensive diagnostic discipline applied by professional behavioral specialists in... Read More
First-order kinetics
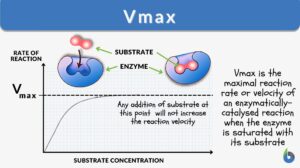
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Renaturation
Definition noun, plural: renaturations (molecular biology) The conversion of denatured protein or nucleic acid to its native... Read More