Search Results for: multicellular
A New Theory on the Origin of Animal Multicellularity
Multicellular life, purportedly, started around 600 million years ago. From single-celled, certain organisms eventually... Read More
Multicellularity
Definition noun A condition or state of having or being composed of many cells or more than one cell performing differing... Read More
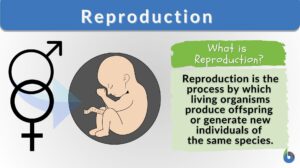
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
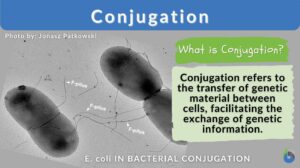
Conjugation
Conjugation generally means the joining or coming together (union), such as in certain unicellular organisms (some bacteria,... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
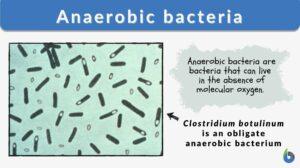
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
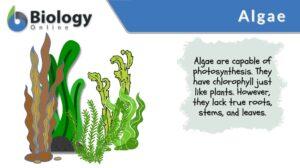
Green algae
Green Algae Definition Green algae (singular: green alga) are photosynthetic algae that are characterized by having... Read More
The Evolutionary Development of Multicellular Organisms
The beginning of the Cambrian era saw a widespread arrival of multi-cellular organisms, particularly in the form of sponges.... Read More
Characteristic
Characteristics Definition We can define characteristics as qualities or features that describe the distinctive nature or... Read More
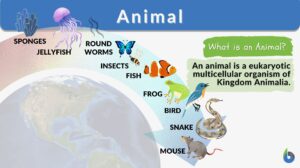
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia Definition Each person can say that they know of or can name at least one animal. However, do people know... Read More
Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta Definition Chlorophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live in marine habitats.... Read More
Bryophytes
Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) do not have xylem or phloem. The habitations of this plant group are widely varied and... Read More
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction involving the fusion of haploid female gamete (egg cell) and haploid male... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Brown algae
Brown Algae Definition Brown algae are algal species characterized by being multicellular and having a brown or... Read More
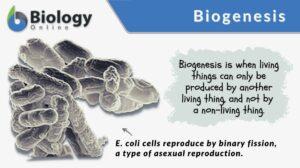
Biogenesis
Biogenesis Definition Biogenesis refers to the idea or the process whereby a living thing comes from another living thing,... Read More
Cell culture
Definition noun, plural: tissue cultures (1) The technique of cultivating cell strains or lines, especially animal cells, in... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More