Search Results for: necessary
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
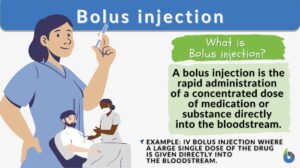
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
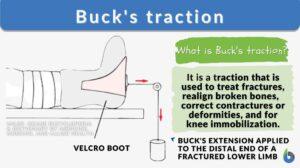
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life ... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
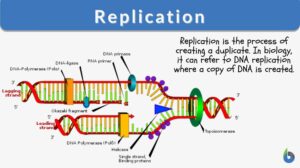
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Environmental resistance
Environmental Resistance Definition Environmental resistance is such a process in which certain different elements or... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Soapsuds enema
Definition The injection of a mixture of water and soap into the colon. Supplement The soapsuds enema uses a mixture of a... Read More
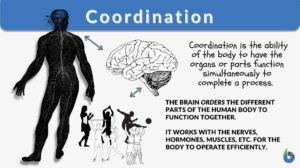
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
Asexual reproduction
Asexual Reproduction Definition What is asexual reproduction? Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not... Read More
At Home in the Universe: The Search for the Laws of Self-Organization and Complexity
At Home in the Universe: The Search for the Laws of Self-Organization and Complexity ... Read More
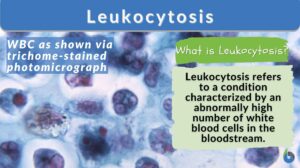
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
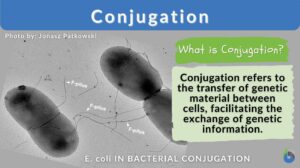
Conjugation
Conjugation generally means the joining or coming together (union), such as in certain unicellular organisms (some bacteria,... Read More
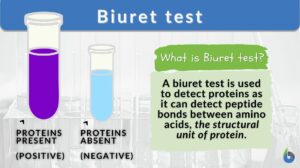
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
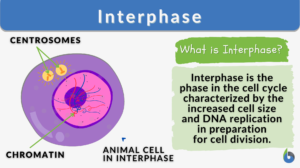
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Directed case study method for teaching human anatomy and physiology
DIRECTED CASE STUDY METHOD FOR TEACHING HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY William H. Cliff and Ann W. Wright Department of... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Abscission
Definition noun (botany) The normal shedding of a senescent plant part or organ (e.g. old leaf or ripe fruit) (zoology) The... Read More