Search Results for: neutral
Neutral mutation
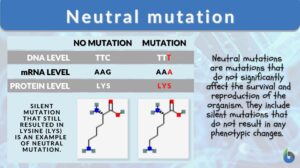
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
Unconditioned stimulus
An unconditioned stimulus inherently triggers an automatic response, not reliant on deliberate prior learning. In contrast... Read More
Neutral dye
Definition noun, plural: neutral dyes (biological techniques) A compound of an acid dye and a basic dye used in staining... Read More
Neutral theory of molecular evolution
Definition noun A theory stating that evolutionary changes particularly at the molecular level arise from genetic drift of... Read More
Neutral stimulus
Definition noun, plural: neutral stimuli In classical conditioning, it is the type of stimulus that initially or normally... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Neutralization
Definition noun (general) The act or process of making neutral. (chemistry) A chemical reaction in which an acid and a base... Read More
Classical conditioning
Definition noun A form of conditioning or associative learning first demonstrated by Ivan Pavlov (a physiologist,... Read More
Neutrophile
Definition noun, plural: neutrophiles (1) A neutrophilic organism that lives and thrives in an environment with a... Read More
Zwitterion
Definition noun, plural: zwitterions A molecule carrying both a positive and a negative charge Supplement A zwitterion is a... Read More
Triglyceride
Definition noun, plural: triglycerides An energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules... Read More
Respondent conditioning
Definition noun A form of conditioning or associative learning first demonstrated by Ivan Pavlov (a physiologist,... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Neutral solution
(Science) Has a pH level of 7: a solution in which the concentration of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions are... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Neutrophil
Definition noun, plural: neutrophils A type of polymorphonuclear leukocyte characterized by having multilobed nucleus,... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Intrinsic protein
Definition noun, plural: intrinsic proteins Any of the group of integral membrane proteins that facilitate specific... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Inorganic salt
Definition noun, plural: inorganic salts A salt that lacks C-H bonds Supplement A salt is defined as the neutral ionic... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Metaprotein
metaprotein Nondescript term for a derived protein obtained by the action of acids or alkalis, soluble in weak acids or... Read More
Adaptive evolution
Definition noun A kind of evolution that involves evolutionary changes that are adaptive to a particular... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More