Search Results for: polarity
Egg polarity gene
Definition noun A maternal gene that encodes for products (mRNA or protein) whose spatial distribution in the egg determines... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
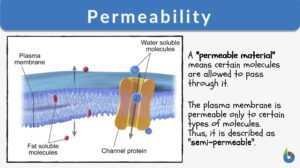
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Polarization
Definition noun (general) The condition of polarity (biology) The process or act of producing positive and negative... Read More
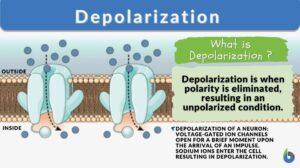
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
Maternal-effect gene
Definition noun, plural: maternal-effect genes (1) A gene from the mother's genome in which its phenotype in the zygote is... Read More
Maternal gene
Definition noun, plural: maternal genes (1) A gene from the mother's genome in which its expression on the phenotype of the... Read More
Pair-rule gene
Definition noun A segmentation gene whose expression subdivides the embryo into a series of stripes, and sets the boundaries... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Microtubule
Microtubule Definition noun plural: microtubules mi·cro·tu·bule, mī'krō-tū'byūl A cytoplasmic tubule made up of... Read More
Polar compound
Definition noun, plural: polar compounds A compound made up of molecules joined by assymetrical polar... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Nonpolar compound
Definition noun, plural: nonpolar compounds A compound comprised of molecules linked through chemical bonds arranged in such... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
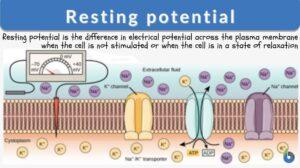
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Polar molecule
Definition noun, plural: polar molecules A molecule with a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges (i.e. having... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Zygotic-effect gene
Definition noun, plural: zygotic-effect genes (1) Any of the genes expressed in the early embryo. (2) Any of the genes... Read More
Ionic bond
Definition noun plural: ionic bonds A type of chemical bond in which atoms, ions, or molecules are held together by... Read More
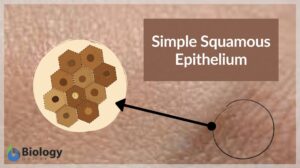
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
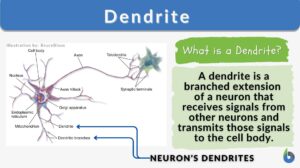
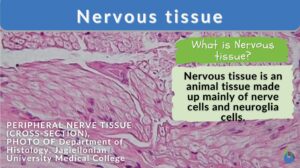
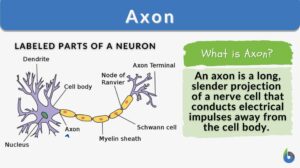
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Hyperpolarization
Definition noun The process or act of making the membrane potential of a cell more negative Supplement Hyperpolarization is... Read More
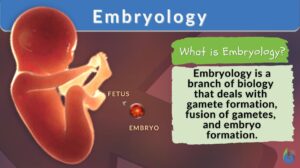
Embryology
Embryology Definition Embryology is a branch of biology that deals with the topics concerning gamete formation... Read More