Search Results for: simple
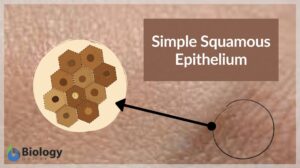
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
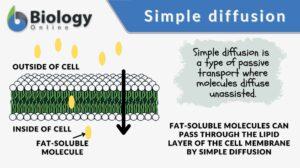
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More
Simple epithelium
Definition noun, plural: simple epithelia An epithelial tissue comprised of a single layer of epithelial cells that are in... Read More
Simple columnar epithelium
Definition noun, plural: simple columnar epithelia Simple epithelium composed of columnar epithelial cells Supplement A... Read More
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Definition noun, plural: simple cuboidal epithelia Simple epithelium composed of cuboidal epithelial cells Supplement A... Read More
Simple fruit
Definition noun, plural: simple fruits A type of fruit that develops from a single or compound ovary with only one pistil... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Simple protein
simple protein protein that yields only alpha-amino acids or their derivatives by hydrolysis; e.g., albumins, globulins,... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
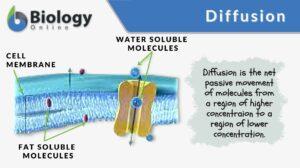
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Epithelium
An epithelium is a type of animal tissue made up of densely packed cells (called epithelial cells) that rest on a basement... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
At Home in the Universe: The Search for the Laws of Self-Organization and Complexity
At Home in the Universe: The Search for the Laws of Self-Organization and Complexity ... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Passive transport
Passive transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances such as ions and molecules move down their respective... Read More
Stratified columnar epithelium
A stratified columnar epithelium (plural: stratified columnar epithelia) is a type of stratified epithelium in which the... Read More
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Definition noun, plural: pseudostratified columnar epithelia A special type of columnar epithelium composed of a single... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
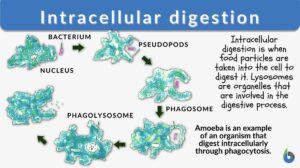
Intracellular digestion
Intracellular Digestion Definition What is intracellular digestion? ‘Intra’ means "inside" and ‘cellular’ pertains... Read More
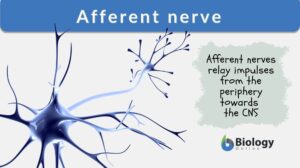
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
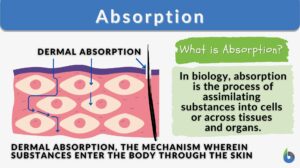
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More
Hypothesis
What Is Hypothesis? A scientific hypothesis is a foundational element of the scientific method. It's a testable statement... Read More
Squamous epithelium
Definition noun, plural: squamous epithelia An epithelial tissue comprised of squamous cells, as seen in epidermis,... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More