Search Results for: spontaneous mutation
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Spontaneous Mutation
A 'naturally' occurring mutation in the absence of a mutagen that would otherwise be a known factor for inducing a... Read More
Natural mutation
natural mutation --> spontaneous mutation A mutation which occurs by itself without first being affected by a mutagen,... Read More
Genetic diversity
Genetic Diversity Definition Each species is composed of individuals with their own set of genes. A gene is the inheritance... Read More
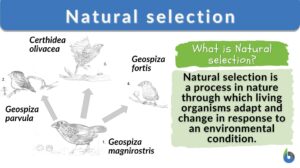
Natural selection
Natural Selection Definition What is natural selection in biology? Natural selection is defined as a process in nature... Read More
Mutagenesis
Definition noun (1) An act of mutating process through changing the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome (2) The... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Haemophilia A
Definition noun A form of haemophilia that is caused by a deficiency in blood clotting factor VIII due to a gene defect in... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is a type of breeding or mating where closely related individuals with a common ancestor produce progenies with... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Thymidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More








![Biology n., [baɪˈɑlədʒi] Definition: scientific study of life](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/biology-definition-and-branches-of-biology-300x168.jpg)
