Search Results for: tension
Surface tension
Surface tension The expression of intermolecular attraction at the surface of a liquid, in contact with air or another gas,... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Hypertonicity
Definition noun The state of being hypertonic, i.e. having a greater degree of tone or tension Supplement In biology,... Read More
Hypotonicity
Definition noun The state of being hypotonic, i.e. having lesser degree of tone or tension Supplement In biology, tonicity... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Abiotic Factors – Water Conditions
Evidently, the light and heat from the sun play an important role in providing suitable conditions. However, the water... Read More
Isotonicity
Definition noun The state of being isotonic, or having equal tension or tonicity Supplement In biology, tonicity pertains to... Read More
Antagonistic Muscle
Definition of Antagonistic Muscle What does the term “antagonistic” mean? As the name suggests, the word antagonistic... Read More
Control of Body Movement
Motor Control Hierarchy A motor program is the pattern of neural activities required to perform a movement is created and... Read More
Capillary action
Definition noun The movement of a liquid, e.g. water molecules, through a narrow space as a result of cohesion, adhesion,... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Cohesion Tension Theory
The hypothesis used to explain how water can travel upwards against gravity in a plant. Transpiration is believed to play a... Read More
Muscle tonus
Definition noun (1) The muscle in a steady partially contracted state caused by the successive flow of nerve... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Sickle cell anaemia
Definition noun A hereditary blood disorder resulting in anaemia due to a mutation in the allele coding for the beta chain... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Nervous dyspepsia
nervous dyspepsia dyspepsia associated with nervousness, tension, or anxiety. Synonym: functional... Read More
Smooth muscle relaxant
smooth muscle relaxant An agent, such as an antispasmodic, bronchodilator, or vasodilator, that reduces the tension or tone... Read More
Phloem fiber
Definition noun (botany) The elongated sclerenchyma cells in the phloem, and is responsible for providing tension strength... Read More
Thalassophobia
Among many psychological and psychiatric disorders, one is the fear of the ocean and the fear of deep water, which in... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
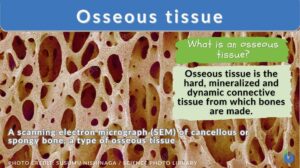
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Water potential
Definition noun The measure of the relative tendency of water to move from one area to another, and is commonly represented... Read More
Muscle tone
Definition noun (1) The muscle in a steady partially contracted state caused by the successive flow of nerve... Read More