Search Results for: transient
Polymorphism
Polymorphism Definition The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred... Read More
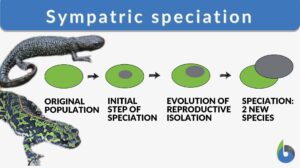
Sympatric speciation
Speciation is a process of evolution through which two different existing populations evolve and a distinct species form. It... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
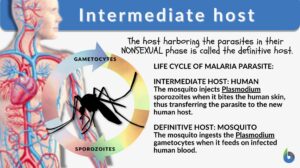
Intermediate host
Intermediate Host Definition When looking at the relationships amongst different biological members of our biosphere, we... Read More
Secular equilibrium
secular equilibrium A type of radioactive equilibrium in which the half-life of the precursor (parent) radioisotope is so... Read More
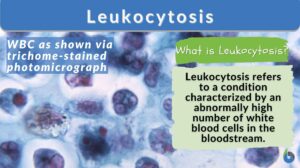
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
Dicrotic notch
Definition noun 1. The brief rise or upstroke in a pulse tracing that occurs before the dicrotic wave, and represents a... Read More
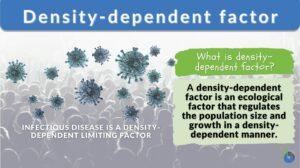
Density dependent factor
Density-dependent factors are the limiting factors of an ecosystem that regulate population growth in a density-dependent... Read More
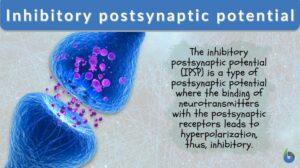
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Overshoots
overshoot 1. Generally, any initial change, in response to a sudden step change in some factor, that is greater than the... Read More
Sonoporation
Definition noun A mechanical method of delivering molecules into the cell using sound, e.g. ultrasonic... Read More
Linea nigra
Definition noun (1) A long narrow dark streak running along the midline of the abdomen, from the umbilicus to the pubis (2) ... Read More
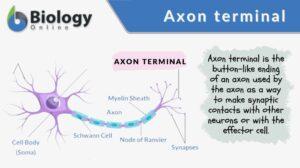
Axon terminal
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
Hydrogen bond
Definition noun plural: hydrogen bonds A type of chemical bond that is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of... Read More
Diglyceride
Definition noun, plural: diglycerides A glyceride consisting of a glycerol and two fatty acid molecules joined through ester... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Signal sequence
Definition noun A sequence of amino acid residues bound at the amino terminus of a nascent protein during protein... Read More
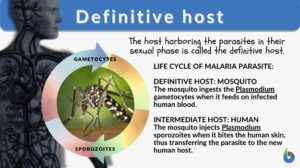
Definitive host
Different Biological Relationships The biological world is interconnected whether we notice it or not. All the life forms... Read More
Accommodation
Accomodation, in general sense, may refer to the dwelling or a transient lodging. In biology, it refers to an adjustment or... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
The Psychobiology of Hysteria
Editorial Hysteria is often regarded as the archetypal psychodynamic illness. Freud carried out much of his early work on... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Loose associations
Definition of Loose Associations When asked to define loose associations in psychology one can tell that it is a formal... Read More