Search Results for: white blood cell
White blood cell
Definition noun, plural: white blood cells Any of the nucleated blood cells that lack hemoglobin, with a primary role in the... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
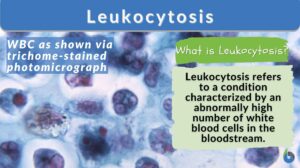
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Blood cell
Definition noun, plural: blood cells Any of the cells in blood, i.e. a red blood cell (erythrocyte) or a white blood cell... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Red blood cell
Definition noun, plural: red blood cells The blood cell containing hemoglobin and functions primarily to transport... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Spongy bone
Spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone or trabecular bone, is a type of bone tissue found at the ends of long bones and... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
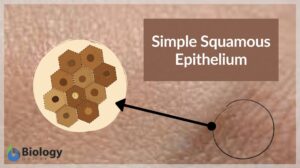
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
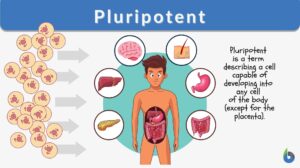
Pluripotent
Pluripotent Definition What is pluripotent? In biology, the term "pluripotent" means capable of developing into... Read More
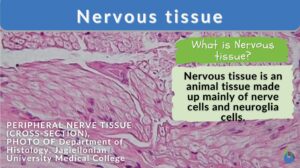
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Plasma volume
Definition noun The total volume of the blood plasma in the circulatory system Supplement The blood is comprised of plasma... Read More
Macrophage
Definition noun, plural: macrophages A leukocyte whose main function is to eliminate cellular debris and foreign particles... Read More
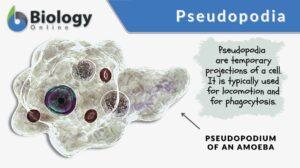
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Pathobiology of allergy and its most severe form, anaphylaxis
When allergy season looms, some people with serious hypersensitivity to allergens tend to be apprehensive of what may come.... Read More
T-helper cell
Definition noun, plural: T-helper cells A type of T lymphocyte that assists by activating antigen-presenting leukocytes,... Read More
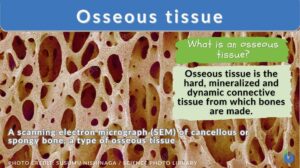
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Lymphocyte
Definition noun, plural: lymphocytes The white blood cell of the blood derived from the stem cells of the lymphoid series of... Read More
Granulocyte
Definition noun, plural: granulocytes A leukocyte characterized by the presence of numerous staining granules in the... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Biological Cell Defense
Organisms must find a means of defense against antigens such a viruses described on the previous tutorial. If this was not... Read More