Search Results for: harvesting
Harvesting
Harvesting 1. (Science: cell culture) The collecting of cells, organisms, or the growth medium upon which an experimental... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
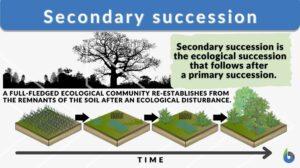
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Mātauranga Māori and Science
By: Maria Victoria Gonzaga In the previous lesson, we learned about the various methods used in measuring... Read More
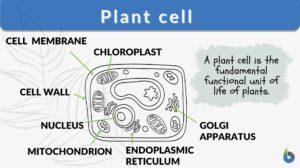
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
Chlorosome
Chlorosome is a photosynthetic micro-compartment that serves as a light-harvesting complex in sulfur bacteria and other... Read More
Cork cambium
Cork Cambium Definition Cork cambium is a secondary meristematic tissue that has a pivotal role in secondary growth in... Read More
Accessory pigment
Definition noun, plural: accessory pigments A non-chlorophyll pigment inside the chloroplast of photosynthetic organisms,... Read More
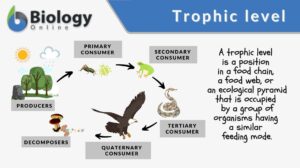
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
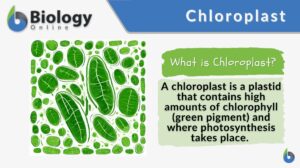
Chloroplast
Chloroplast Definition What is chloroplast? In biology, a chloroplast refers to the organelle found within the cell of... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Light reactions
Definition noun The series of biochemical reactions in photosynthesis that require light energy that is captured by... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More