Search Results for: inorganic
Inorganic compound
Inorganic Compound Definition An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and... Read More
Inorganic molecule
Definition noun, plural: inorganic molecules (1) A molecule not consisting of carbon atoms. (2) Any molecule that is not... Read More
Inorganic salt
Definition noun, plural: inorganic salts A salt that lacks C-H bonds Supplement A salt is defined as the neutral ionic... Read More
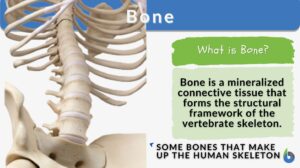
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Inorganic catalyst
Definition noun, plural: organocatalysts An inorganic compound used as a catalyst. Supplement Inorganic catalysts speed up a... Read More
Heterotroph
Heterotroph Definition What is a heterotroph? Does a heterotroph make its own food? In biology and ecology, a heterotroph... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
Chemotroph
Chemotroph Definition A chemotroph refers to an organism that obtains energy mainly from carbon dioxide and from... Read More
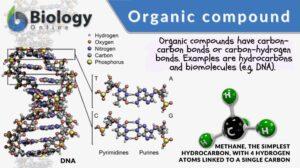
Organic compound
Organic Compound Definition An organic compound is a compound that, in general, contains carbon covalently bound to other... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
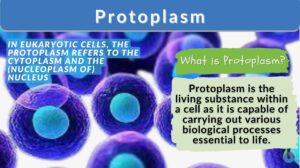
Protoplasm
Protoplasm Definition The protoplasm is regarded as "the living material or the living content of a cell". It is fluid... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Bone tissue
Definition noun, plural: bone tissues A mineralized connective tissue from which bones are made. Supplement The bone tissue... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More
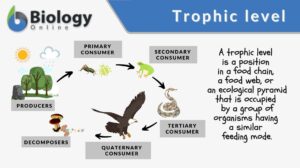
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
Primary consumer
Definition noun, plural: primary consumers Any organism that consumes or feeds on autotrophs Supplement A food chain is... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Primary producers
'Primary producers (also called simply as producers) are the autotrophs capable of producing organic compounds from light... Read More