Search Results for: legumes
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
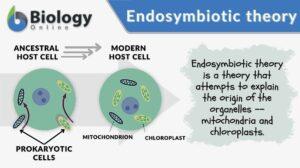
Endosymbiotic theory
A eukaryotic cell is distinct from a prokaryotic cell by the presence of membrane-bound cellular structures called... Read More
Endosymbiosis
Definition noun A symbiosis wherein the symbiont lives within the body of its host Supplement Symbiosis pertains to a close... Read More
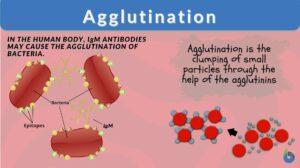
Agglutination
Agglutination Definition What does agglutination mean? It generally refers to the process of sticking together or the... Read More
Root nodules
Root nodule (Science: plant biology) globular structure formed on the roots of certain plants, notably legumes and alder, by... Read More
Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
Through genetic engineering, scientists are able to move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
Alphaproteobacteria
Definition noun A taxonomic class belonging to the phylum Proteobacteria that includes phototropic proteobacteria,... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
Biology: Concepts & Connections with Student CD-ROM (5th Edition)
Biology: Concepts & Connections with Student CD-ROM (5th Edition) ... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
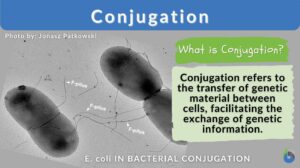
Conjugation
Conjugation generally means the joining or coming together (union), such as in certain unicellular organisms (some bacteria,... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Methods of Breaking Seed Dormancy
Definition of Seed Dormancy: Non – germination of seeds due to absence of suitable conditions is termed as dormancy.... Read More