Search Results for: metabolism
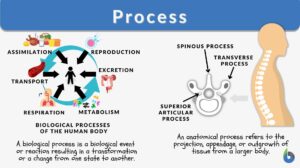
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Metabolic pathway
Definition noun A series of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes and are connected by their intermediates, i.e. the... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Intermediary metabolism
Definition noun The intermediate steps within the cells in which the nutrient molecules or foodstuffs are metabolized and... Read More
Respiratory metabolism
respiratory metabolism The exchange of respiratory gases in the lungs, oxidation of foodstuffs in the tissues, and... Read More
Oxidative metabolism
oxidative metabolism respiration in the biochemical... Read More
Calcium metabolism
Calcium metabolism a set of biochemical processes which act to keep the level of calcium in the blood at a constant level,... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Metabolic disorder
Definition noun, plural: metabolic disorders A disorder in the metabolism, often caused by a dysfunctional enzyme as a... Read More
Characteristic
Characteristics Definition We can define characteristics as qualities or features that describe the distinctive nature or... Read More
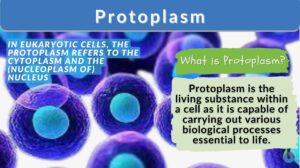
Protoplasm
Protoplasm Definition The protoplasm is regarded as "the living material or the living content of a cell". It is fluid... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
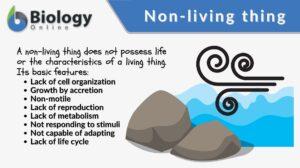
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More