Search Results for: protoplasm
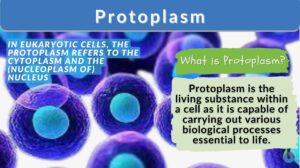
Protoplasm
Protoplasm Definition The protoplasm is regarded as "the living material or the living content of a cell". It is fluid... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Streaming movement
streaming movement The form of movement characteristic of the protoplasm of leukocytes, amoebae, and other unicellular... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Cell inclusion
Definition noun, plural: cell inclusions Any of the nonliving materials in the cell protoplasm Supplement Examples of cell... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
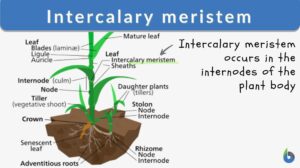
Intercalary meristem
The basic structural framework of plants is composed of different types of tissues. Based upon the capacity to divide, the... Read More
Karyostenosis
Karyostenosis (Science: biology) direct cell division (in which there is first a simple division of the nucleus, without any... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
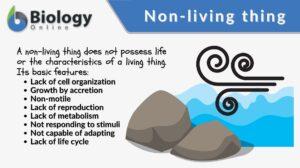
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More
Middle lamella
Definition noun plural: middle lamellae ˈmɪdəl ləˈmɛl.ə A pectin-rich intercellular material that glues the... Read More
Secondary cell wall
Definition noun plural: secondary cell walls ˈsɛkənˌdɛɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms... Read More
Genome shuffling
Recombination of whole genomes. One example is protoplasm... Read More
Primary cell wall
Definition noun plural: primary cell walls ˈpɹaɪməɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms prior to... Read More
Plasmodium
plasmodium (Science: plant biology) Multinucleate mass of protoplasm bounded only by a plasma membrane, the main vegetative... Read More
Nonseptate mycelium
Nonseptate mycelium One in which there are no septa, or cross-walls, in the hyphae; inasmuch as the latter is not divided... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More