Search Results for: reacts
Prostaglandin F2-alpha
Definition noun, plural: prostaglandins F A biologically active prostaglandin that forms when the intermediate prostaglandin... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Deoxyribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: deoxyribonucleotides de·ox·y·ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, diˌɒk... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Luciferase
Definition noun, plural: luciferases Any of the group of enzymes that act on the oxidation of luciferin of bioluminescent... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Plant Cell Defense
Hydrogen Peroxide Plants release hydrogen peroxide in response to the presence of a fungal invasion, which attacks by... Read More
Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the means that primary producers (mostly plants) can obtain energy via light energy. The energy gained... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Chelating agent
Definition noun, plural: chelating agents A ligand, often an organic compound, which reacts with a metal ion to produce a... Read More
Edman degradation
Definition noun A method of sequencing amino acids of a peptide through a reagent that reacts with the peptide at the... Read More
Jaw jerk reflex
Definition noun A stretch reflex that manifests as the contraction of the masseter and the temporalis muscles in response to... Read More
Patellar reflex
Definition noun, plural: patellar reflexes A stretch reflex wherein the anterior muscles of the thigh contracts by reflex as... Read More
Achilles reflex
Definition noun, plural: Achilles reflexes A stretch reflex wherein the foot jerks towards the plantar surface by reflex as... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Adenine nucleotide
Definition noun plural: adenine nucleotides A nucleotide wherein the nucleobase is adenine Details Overview A nucleotide... Read More
Guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Cytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Deoxycytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxycytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Thymidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
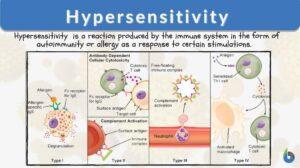
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity Definition Hypersensitivity is the exaggerated immune response to protect the human from foreign bodies... Read More
Glyceraldehyde phosphate
Definition noun A phosphate ester of the 3-carbon sugar glyceraldehyde and has chemical formula:... Read More