Search Results for: ammonia
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Ammonotelism
Ammonotelism The excretion of ammonia and ammonium ions is calles ammonotelism. The organisms which excrete by ammonotelism... Read More
Nitrifying bacterium
Definition noun, plural: nitrifying bacteria A bacterium that is capable of converting ammonium into... Read More
Nitrogen fixation
Definition noun The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a more usable form by natural means, such as by the... Read More
Unsaturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: unsaturated fatty acids The unsaturated fatty acid is a form of fatty acid containing one or more... Read More
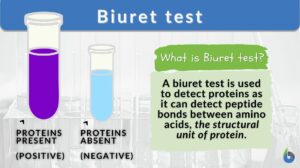
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Abiotic Fixation
Definition noun It is part in nitrogen cycle wherein atmospheric nitrogen fixation carries out non-living components to... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
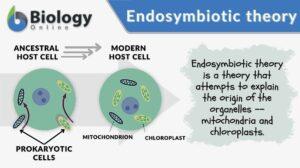
Endosymbiotic theory
A eukaryotic cell is distinct from a prokaryotic cell by the presence of membrane-bound cellular structures called... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Cytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
Cytidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is composed of cytidine (a cytosine... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
“Mutualism factor” could explain why body does not attack normal flora
When sadness reeks in and you feel as if you are all by yourself, think again. That is because you are never alone. As a... Read More
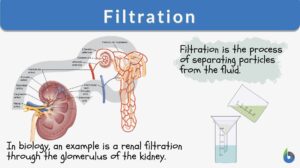
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Nitrosomonas
nitrosomonas A genus of gram-negative, ellipsoidal or rod-shaped bacteria whose major source of energy and reducing power is... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Photorespiration
Definition noun (1) The process by which in the presence of light plant consumes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide (in... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More