Search Results for: carbohydrates
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Alongside the numerous vitamins that are required as part of a healthy diet, we must also eat food containing a variety of... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
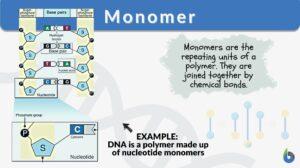
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Human Biology – Food and Digestion
Food is what is required by humans to grow and survive, and provide a 'fuel' for the energy needed in our biological... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Galacto-oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: galacto-oligosaccharides ga·lac·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride An oligosaccharide made up of... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More