Search Results for: enzyme regulation
Enzyme regulation
Enzyme regulation (Science: biochemistry) control of the rate of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme by some effector (e.g.,... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Some genes are switched on or off depending on environmental conditions. The... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
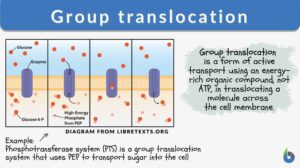
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of adenosine monophosphate that... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Regulatory gene
Definition noun, plural: regulatory genes A gene that is involved in the production of a substance that controls or... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More