Search Results for: osmosis
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Plant Water Regulation
A plant requires water as an essential ingredient of photolysis, the photochemical stage of photosynthesis where water is... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
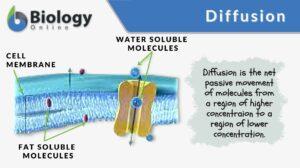
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Animal Water Regulation
Homeostatic control, a set environment, and how evolution and natural selection drives a species to adapt to its environment... Read More
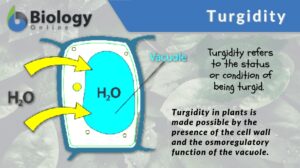
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
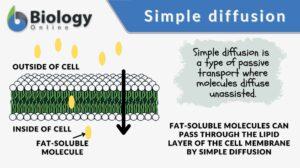
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More
Passive transport
Passive transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances such as ions and molecules move down their respective... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Osmotic lysis
Definition noun The bursting or rupturing of cell membrane due to osmotic movement of water into the cell when the cell... Read More
Water potential
Definition noun The measure of the relative tendency of water to move from one area to another, and is commonly represented... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Hyposmotic
Definition adjective 1. Of, relating to, or characterized by having a lower osmotic pressure than a surrounding fluid under... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
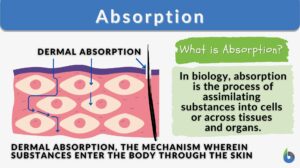
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More
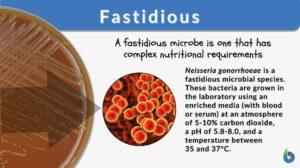
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
Desiccation
Desiccation definition Desiccation refers to the state, the act, or the process of removing or extracting water content... Read More
Contractile vacuole
Definition noun, plural: contractile vacuoles (cell biology) A specialized vacuole of eukaryote cells, especially protozoa,... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More

![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)