Search Results for: velocity
Macrophytes
Introduction Examples of Macrophytes. (Source: Canada's AquaticEnvironments) ... Read More
Running Water Freshwater Communities
Running water freshwater communities are also known as lotic communities, lotic meaning running water. Lotic communities are... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
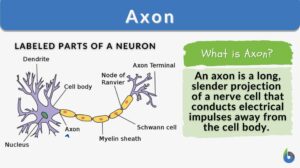
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
Freshwater Ecology
Freshwater ecology focuses on the relations of aquatic organisms to their freshwater habitats. There are two forms of... Read More
Linear acceleration
Linear acceleration The rate of change of velocity without a change in direction; e.g., when the speed of an aircraft... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Shifted maxwellian
shifted maxwellian (Science: radiobiology) distribution function of the form Exp-((v-u)/v-thermal)^2, where the ordinary... Read More
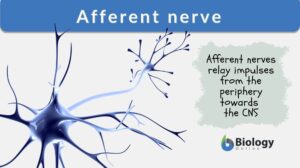
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
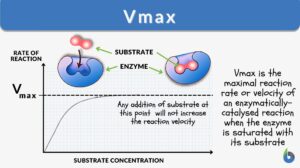
Eadie-hofstee plot
Eadie-hofstee plot (Science: biochemistry) a graphical representation of enzyme kinetic data in which the velocity of the... Read More
Boundary layer
Boundary layer (Science: radiobiology) in fluid flow, a narrow region next to a fixed boundary or surface where the fluid... Read More
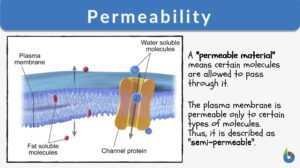
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More