Search Results for: yields
Milk yields affected by music tempo
Dairy cows produce more milk when listening to REM's 'Everybody Hurts' or Beethoven's 'Pastoral Symphony' than when... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Sphingolipid
Definition noun plural: sphingolipids sphin·go·lip·id A type of lipid with a sphingoid base (e.g. sphingosine and... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway
Definition noun A glycolytic pathway whereby glucose is metabolized and converted ultimately to pyruvate, and results in a... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Selective Breeding
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, PhD Thousands of years before Darwin proposed evolution by natural selection and... Read More
Cytidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is composed of cytidine (a cytosine... Read More
Simple protein
simple protein protein that yields only alpha-amino acids or their derivatives by hydrolysis; e.g., albumins, globulins,... Read More
Cerebroside
Definition noun, plural: cerebrosides A glycosphingolipid made of a monosaccharide or an oligosaccharide linked... Read More
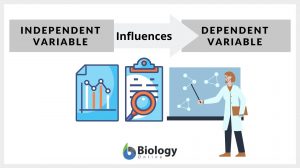
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Glycolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycolipids A carbohydrate, usually an oligosaccharide, that is covalently linked to a lipid... Read More
Glycosphingolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycosphingolipids A type of glycolipid made up of a glycan (or a carbohydrate) linked to the... Read More
Guanosine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is composed of guanosine (a... Read More
Cytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life ... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Kiliani-fischer synthesis
Kiliani-fischer synthesis a synthetic procedure for the extension of the carbon atom chain of aldoses by treatment with... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Enhancement effect
Enhancement effect property of higher plant photosynthesis, discovered by robert Emerson. The quantum yield of red light... Read More
Obligate aerobe
Before we define obligate aerobes, let us first understand and define aerobic organisms. Aerobic organisms are those that... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Cortex glandulae suprarenalis
Cortex glandulae suprarenalis --> suprarenal cortex the outer part of the adrenal gland, consisting of three zones from... Read More