Search Results for: crystalline
Proteinoplast
Definition noun, plural: proteinoplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores and modifies protein Supplement Plastids are... Read More
Chromoplast
Definition noun, plural: chromoplasts Any of the coloured plastids associated with pigment synthesis and... Read More
Sodium hydrogen carbonate
sodium hydrogen carbonate --> sodium bicarbonate (Science: chemical) carbonic acid monosodium salt (CHNaO3). A white,... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Sodium bicarbonate
sodium bicarbonate (Science: chemical) carbonic acid monosodium salt (CHNaO3). A white, crystalline powder that is used as... Read More
Stereospecificity
Definition noun Relate to the specific points along the chain of configurations resulting in the spatial arrangement of... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
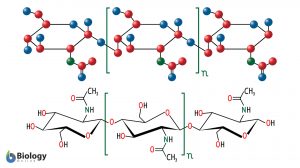
Cellobiose
Definition noun plural: cellobioses cel·lo·bi·ose, ˌsɛləʊˈbaɪəʊz A disaccharide made up of two glucose... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Ionic bond
Definition noun plural: ionic bonds A type of chemical bond in which atoms, ions, or molecules are held together by... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
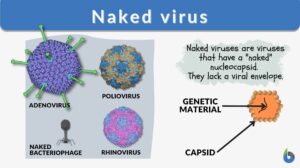
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
Methionine
methionine (Science: biochemistry) Contains the SCH3 group that can act as a methyl donor (see s adenosyl methionine).... Read More
Inclusion bodies
Inclusion bodies (Science: cell biology) nuclear or cytoplasmic structures with characteristic staining properties, usually... Read More
Lenticular
Lenticular 1. (Science: anatomy) Pertaining to or shaped like a lens. 2. (Science: ophthalmology) Pertaining to the... Read More
Efflorescence
Definition noun (1) (botany) The state of efflorescing; time of flowering or blossoming; anthesis. (2) (medicine) A... Read More