Search Results for: cytosol
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Intracellular fluid
Definition noun The body fluid within the cell composed mainly of water dissolved ions, and other molecules Supplement The... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Fatty acid
Definition noun plural: fatty acids'' fatty acid, ˈfætɪ ˈæsɪd Any of the group of a long chain of hydrocarbon... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
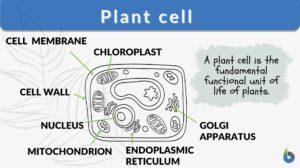
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Steroid hormone
Definition noun, plural: steroid hormones A type of steroid that acts as a hormone, and that which is exemplified by sex... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: ribosomal ribonucleic acids ri•bo•so•mal ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈraɪ... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More