Search Results for: degrees
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom in statistics, the number of independent comparisons that can be made between the members of a sample... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Thermometer
thermometer (Science: physics) An instrument for measuring temperature, founded on the principle that changes of temperature... Read More
Petrified Wood : The World of Fossilized Wood, Cones, Ferns, and Cycads
Petrified Wood : The World of Fossilized Wood, Cones, Ferns, and Cycads ... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
Graduation
Graduation 1. The act of graduating, or the state of being graduated; as, graduation of a scale; graduation at a college;... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Homeostatic equilibrium
Definition noun (1) The tendency of an organism or a cell to regulate its internal conditions, usually by a system of... Read More
Sex-linked trait
Definition of Sex-Linked Traits A sex-linked trait is an observable characteristic of an organism that is influenced by the... Read More
Ecosystem diversity
Ecosystem Diversity Definition What is ecosystem diversity? Ecosystem diversity deals with the study of different... Read More
Methanotroph
Definition noun, plural: methanotrophs An organism that metabolize methane as a source of carbon and... Read More
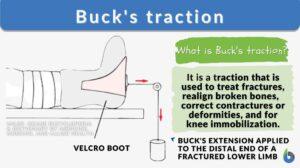
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
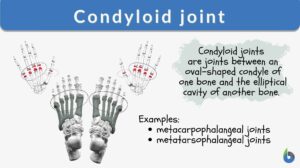
Condyloid joint
A joint is a point where two bones are attached and are capable of movement. The joints not only provide the movements of... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Corticosteroid
Definition noun, plural: corticosteroids A steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex, e.g. glucocorticoids and... Read More
Cell junction
Definition noun, plural: cell junctions Intercellular connections between adjacent cells, resulting in varying degrees of... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Xxy syndrome
XXY syndrome --> klinefelter's syndrome (Science: syndrome) A condition characterised by small testes with hyalinization... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Control of Body Movement
Motor Control Hierarchy A motor program is the pattern of neural activities required to perform a movement is created and... Read More