Search Results for: motility
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
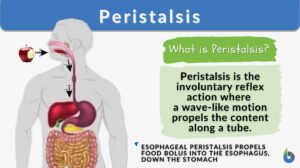
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis Definition Spermatogenesis is the biological process of producing sperm cells. It occurs in the male gonad... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
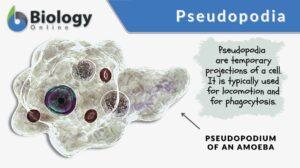
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Nervous colon syndrome
nervous colon syndrome (Science: syndrome) A common gastrointestinal disorder characterised by abdominal pain, bloating,... Read More
Human Reproduction
Terminology and Concepts Primary reproductive organs are called gonads - testes in the male and ovaries in the female.... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
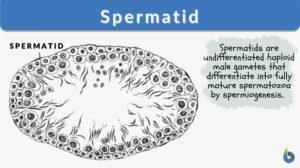
Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis Definition Spermiogenesis is the stage of spermatogenesis wherein the spermatids differentiate into mature... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Adenine nucleotide
Definition noun plural: adenine nucleotides A nucleotide wherein the nucleobase is adenine Details Overview A nucleotide... Read More
Guanosine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is composed of guanosine (a... Read More
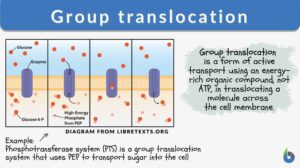
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More