Search Results for: prokaryote
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Prokaryotic cell
Definition noun, plural: prokaryotic cells (1) The cell of a prokaryote, i.e. an organism whose cell generally lacks a true... Read More
Euchromatin
Definition noun A slightly packed or partially condensed form of chromatin that contains structural genes and is usually... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Oxidative phosphorylation
Definition noun A metabolic pathway that generates ATP from ADP through phosphorylation that derives the energy from the... Read More
Charophyta
Charophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live predominantly in freshwater habitats. Members... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Eukaryotic cell
Definition noun, plural: eukaryotic cells The cell of a eukaryote, i.e. an organism that possesses a membrane-bound... Read More
Prokaryotic Ancestor of Mitochondria: on the hunt
The alphaproteobacteria have been widely cited as the closest relative-- and possibly the prokaryotic ancestor -- of the... Read More
Methanotroph
Definition noun, plural: methanotrophs An organism that metabolize methane as a source of carbon and... Read More
Thermophile
Thermophiles Definition What are thermophiles? Let us first understand the literal meaning of the word ‘thermophile’.... Read More
Glycosidase
Definition noun, plural: glycosidases (biochemistry) An enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of a... Read More
DNA polymerase
Definition noun, plural: DNA polymerases (molecular biology) An enzyme assisting in DNA replication Supplement Polymerases... Read More
DNA polymerase I
Definition noun The first known DNA polymerase, encoded by polA gene, and is involved in DNA replication in... Read More
DNA polymerase II
Definition noun A DNA polymerase involved in DNA replication in prokaryotes, is encoded by polB gene, and composed of 783... Read More
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: ribosomal ribonucleic acids ri•bo•so•mal ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈraɪ... Read More
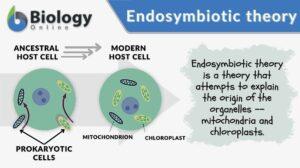
Endosymbiotic theory
A eukaryotic cell is distinct from a prokaryotic cell by the presence of membrane-bound cellular structures called... Read More
Magnetosome
Definition noun, plural: magnetosomes A membranous cytoplasmic structure containing mineral crystals that enable certain... Read More
Bacterioplankton
Definition noun The bacterial component of plankton of aquatic ecosystems Supplement Plankton pertain to the small organisms... Read More
Messenger ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: messenger ribonucleic acids mes•sen•ger ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈmɛ.sɪn.dʒəɹ... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta Definition Chlorophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live in marine habitats.... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More