Search Results for: wheat
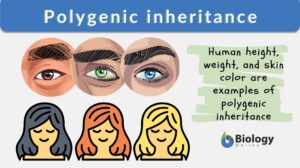
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Abiogenesis
Definition noun plural: abiogeneses a·bi·o·gen·e·sis, eɪbaɪəʊˈdʒɛnəsɪs (1) The idea that primitive life... Read More
Allopolyploidy
Definition noun (genetics) A type of euploidy wherein the additional set of chromosomes is derived from another species,... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Recalcitrant
Several words of the English language find wide usage in subjects as diverse as literature, science, social science,... Read More
Allotetraploid
Allotetraploid Definition An allotetraploid is an organism with four sets of chromosomes (4n). This is in contrast to the... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
Vertical gene transfer
Definition noun (genetics) The transfer of genes from parents to offspring Supplement Gene transfer refers to the movement... Read More
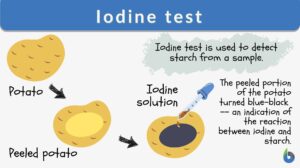
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Simple fruit
Definition noun, plural: simple fruits A type of fruit that develops from a single or compound ovary with only one pistil... Read More
Binomial nomenclature
Binomial Nomenclature Definition Binomial nomenclature is a binomial system of naming a species. A binomial name is... Read More
Polyploidy
Definition noun (genetics) The state of being polyploid, that is more than two sets of the chromosomes in a... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
Through genetic engineering, scientists are able to move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or... Read More
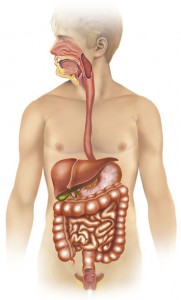
How Celiac Disease Affects The Digestive System
Celiac disease is a condition that affects the digestive systems of many individuals all over the world, and in this... Read More
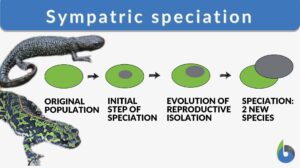
Sympatric speciation
Speciation is a process of evolution through which two different existing populations evolve and a distinct species form. It... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
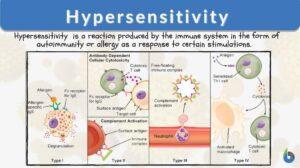
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity Definition Hypersensitivity is the exaggerated immune response to protect the human from foreign bodies... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More