Search Results for: adhesion
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Capillary action
Definition noun The movement of a liquid, e.g. water molecules, through a narrow space as a result of cohesion, adhesion,... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Plant Water Regulation
A plant requires water as an essential ingredient of photolysis, the photochemical stage of photosynthesis where water is... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
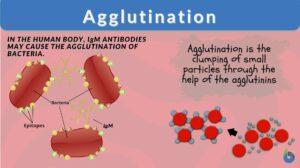
Agglutination
Agglutination Definition What does agglutination mean? It generally refers to the process of sticking together or the... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Adsorption
Adsorption 1. (Science: chemistry) The accumulation or concentration of molecules of a gas or liquid on a surface in contact... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Extracellular matrix
Definition noun, plural: extracellular matrices The non-cellular portion of a tissue produced and secreted by cells and... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Cell recognition
Definition noun (1) Mutual recognition between cells, usually by specific complementary interaction between their respective... Read More
Stratum corneum
Definition noun The outermost layer of the epidermis comprised of corneocytes and accounts for most of the protective... Read More
Goniosynechia
Definition noun, plural: goniosynechiae Synechia of the iris to the cornea in the angle of the anterior... Read More
Microvillus
Definition noun, plural: microvilli Any of the minute hairlike structures projecting from the exposed surface of the cell in... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
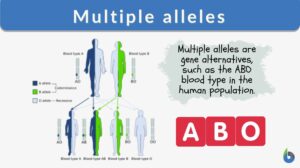
Multiple alleles
Alleles are the pairs of genes occupying a specific spot called locus on a chromosome. Typically, there are only two alleles... Read More
Blood-brain barrier
Definition noun A semipermeable membrane that serves as a selective barrier separating the circulating blood and the... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Glycolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycolipids A carbohydrate, usually an oligosaccharide, that is covalently linked to a lipid... Read More
Glycosphingolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycosphingolipids A type of glycolipid made up of a glycan (or a carbohydrate) linked to the... Read More