Search Results for: causes
Types and Causes of Brain Damage
The brain is a highly specialized tissue, far more complex than today's 21st-century supercomputers. Due to this magnificent... Read More
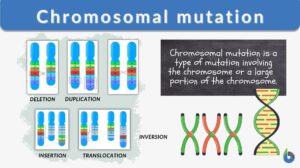
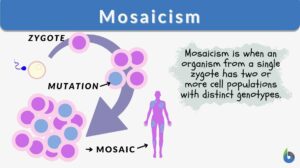
Chromosomal mutation
Every living thing is made up of DNA. Our DNA is what makes us unique and different in the world. Our DNA is made up of... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
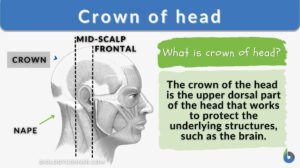
Crown of head
Crown of Head Definition The crown of the head is the upper dorsal part (or area) of the head. Several creatures have... Read More
Allopatric speciation
We can define speciation as a process by which the novel genetically independent group of organisms are formed through the... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
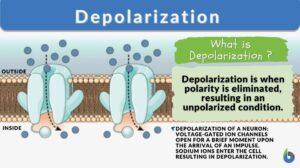
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
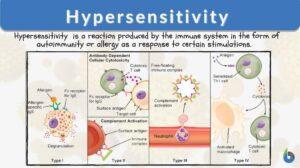
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity Definition Hypersensitivity is the exaggerated immune response to protect the human from foreign bodies... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
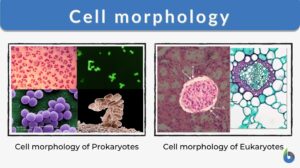
Cell morphology
The basic essence for any living organism is its structural framework which includes appearance, form, and the... Read More
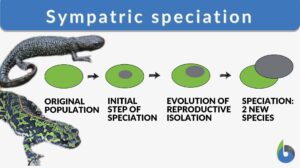
Sympatric speciation
Speciation is a process of evolution through which two different existing populations evolve and a distinct species form. It... Read More
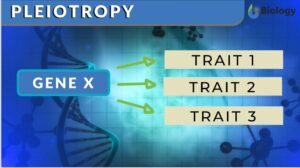
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy Definition When one single gene starts affecting multiple traits of living organisms, this phenomenon is known... Read More
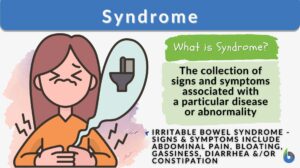
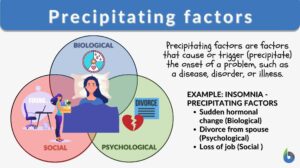
Precipitating factors
Precipitating Factor Definition Precipitating factors are factors that initiate or promote the onset of any illness,... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Thalassophobia
Among many psychological and psychiatric disorders, one is the fear of the ocean and the fear of deep water, which in... Read More
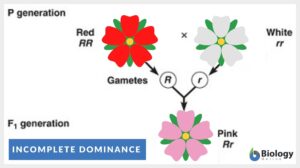
Incomplete dominance
Incomplete Dominance Definition After Gregor Mendel discovered inheritance laws, the term ''incomplete dominance'' was... Read More
Polymorphism
Polymorphism Definition The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred... Read More
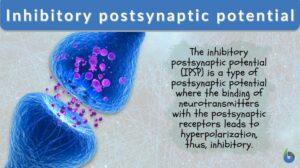
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Blindness – Evolutionary regression? Maybe not!
The recent Netflix's hit flick, Bird Box, surely startled the viewers with the thrilling scenarios revolving around the... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More