Search Results for: cell theory
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
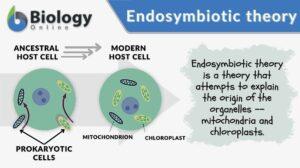
Endosymbiotic theory
A eukaryotic cell is distinct from a prokaryotic cell by the presence of membrane-bound cellular structures called... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
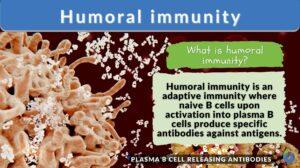
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Theory of Neuroscience
Nezih OKTAR Journal of Neurological Sciences (Turkish) 2006, Volume 23, Number 3, Page(s) 155-158. An Open Access... Read More
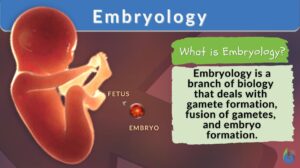
Embryology
Embryology Definition Embryology is a branch of biology that deals with the topics concerning gamete formation... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Prokaryotic Ancestor of Mitochondria: on the hunt
The alphaproteobacteria have been widely cited as the closest relative-- and possibly the prokaryotic ancestor -- of the... Read More
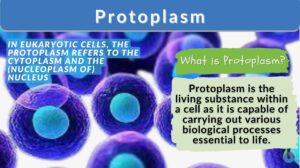
Protoplasm
Protoplasm Definition The protoplasm is regarded as "the living material or the living content of a cell". It is fluid... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
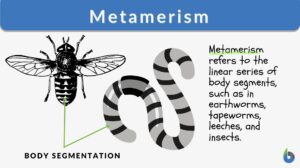
Metamerism
Metamerism Definition Metamerism is the repetition of homologous body segments. This type of development can be seen in the... Read More
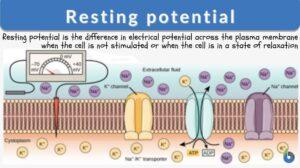
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
A New Theory on the Origin of Animal Multicellularity
Multicellular life, purportedly, started around 600 million years ago. From single-celled, certain organisms eventually... Read More
Law of biogenesis
Law Of Biogenesis Definition Law of Biogenesis states that life arises from pre-existing life, not from nonliving matter.... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
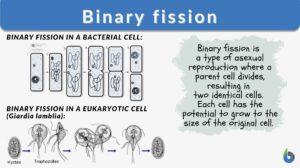
Binary fission
Binary Fission Definition What is binary fission? In biology, binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More

![Biology n., [baɪˈɑlədʒi] Definition: scientific study of life](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/biology-definition-and-branches-of-biology-300x168.jpg)