Search Results for: comes
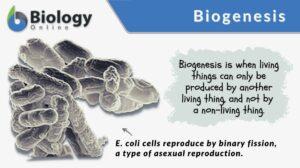
Biogenesis
Biogenesis Definition Biogenesis refers to the idea or the process whereby a living thing comes from another living thing,... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
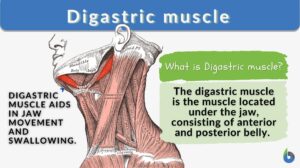
Digastric muscle
Digastric Definition The digastric muscle is a paired muscle located under the jaw, consisting of the anterior and... Read More
Macrophytes
Introduction Examples of Macrophytes. (Source: Canada's AquaticEnvironments) ... Read More
Hermaphrodite
We all know that typically living organisms are divided into two main categories of sex-based on their biological structure.... Read More
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction involving the fusion of haploid female gamete (egg cell) and haploid male... Read More
Gag reflex
Definition noun, plural: gag reflexes A reflex contraction characterized by retching or gagging when a foreign body comes in... Read More
Spontaneous generation
Definition noun plural: spontaneous generations The previously popular notion that living organisms arise or develop from... Read More
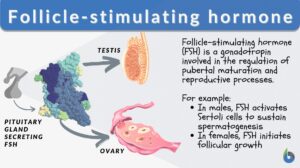
Follicle-stimulating hormone
Follicle Stimulating Hormone Definition In the pituitary gland of the brain, gonadotropic hormones are released.... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Prodromal period
There are five stages (or phases) of a disease. (Hattis, 2020). These stages are (1) Incubation period, (2) Prodromal... Read More
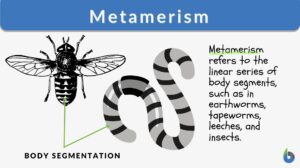
Metamerism
Metamerism Definition Metamerism is the repetition of homologous body segments. This type of development can be seen in the... Read More
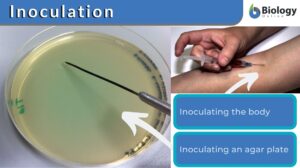
Inoculation
Inoculation Definition In Immunology, inoculation is defined as the process of introducing an antigenic substance or... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
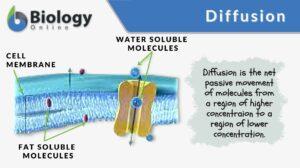
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Apical bud
Apical Bud Definition The apical bud is the type of bud located at the top (apex) of the plant, particularly at the very... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Interspecific competition
Interspecific Competition Definition In Biology, competition is defined as the process that occurs among species that have... Read More
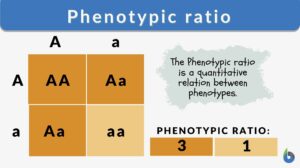
Phenotypic ratio
Phenotypic Ratio Definition How would one define phenotypic ratio? The correlation between the amount of offspring that... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Selective Breeding
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, PhD Thousands of years before Darwin proposed evolution by natural selection and... Read More