Search Results for: cytochrome
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Cell Respiration
As mentioned in the previous tutorial on ATP, the process of respiration is split into 3 distinct areas that occur at... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
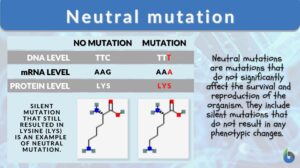
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
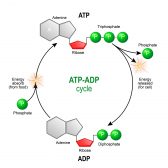
ATP & ADP – Biological Energy
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate, and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. It consists of an... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Testosterone
Definition noun, plural: testosterones A steroid hormone with a chemical formula of C19H28O2, and is regarded as the primary... Read More
Effect of Chemicals on Growth & Development in Organisms
Plants Plants require a large number of elements to function properly, mainly carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, essentially... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Minerals and Proteins
Minerals Various minerals in the Earth's crust are required for a healthy balanced diet. These inorganic compounds have... Read More
Chloroplast DNA
Definition noun plural: chloroplast DNAs DNA in the chloroplast that carries the code for proteins and RNAs essential to... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Lactobacillus casei
Definition noun A non-pathogenic and harmless bacterium recognized widely as probiotics that controls growth of various... Read More
Aldosterone
Definition noun, plural: aldosterones A mineralocorticoid with a chemical formula of C21H28O5, and controls salt and water... Read More
Peripheral membrane protein
Definition noun, plural: peripheral membrane proteins A protein that temporarily adheres to the biological membrane, either... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
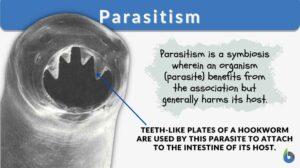
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Dehydrogenase
Dehydrogenase (Science: enzyme) enzyme that oxidizes a substrate by transferring hydrogen to an acceptor that is either... Read More
Enterobacteriaceae
Definition noun: (taxonomy) A family of gram-negative bacilli that inhabit the large intestine of humans and other... Read More