Search Results for: cytosine
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
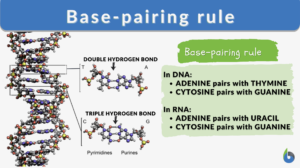
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Cytidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is composed of cytidine (a cytosine... Read More
Thymidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Cytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Deoxycytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxycytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
Previous pages in this tutorial have described the basics of a cell, the energy required by these cells and how energy is... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Deoxyribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: deoxyribonucleotides de·ox·y·ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, diˌɒk... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Deoxycytidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxycytidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, deoxyribose and... Read More
Chargaffs rules
Definition noun The rules proposed by an Austro-Hungarian biochemist, Erwin Chargaff, implicating that the double helical... Read More
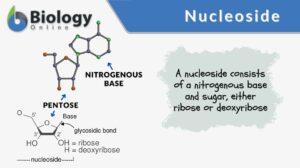
Nucleoside
Nucleoside Definition A nucleoside is a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bound to a pentose sugar ribose or... Read More
Erwin Chargaff
Quick Info (person) A biochemist known for his proposed Chargaff's rules that led to the discovery of the double helical... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Base pairing
Base pairing (Science: molecular biology) The specific hydrogen bonding between purines and pyrimidines in double stranded... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
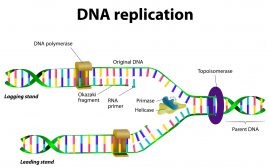
DNA replication
DNA Replication Definition DNA replication is the process of copying and duplicating a DNA molecule. The process is carried... Read More