Search Results for: expression
Expression vector
Definition noun, plural: expression vectors A plasmid containing the required regulatory sequences specifically used for the... Read More
Constitutive expression
Definition noun Expression of a gene that is transcribed at a constant level. Supplement For example, the expression of... Read More
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Expression library
Expression library (Science: molecular biology) a library of dna fragments which was created with an expression vector so... Read More
Expression system
Expression system (Science: molecular biology) combination of an expression vector, its cloned dna, and the host for the... Read More
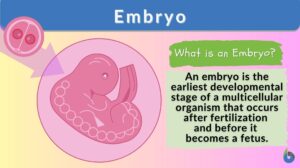
Expression
Expression (Science: molecular biology) The process by which a genes coded information is converted into the structures... Read More
Multiple alleles
Alleles are the pairs of genes occupying a specific spot called locus on a chromosome. Typically, there are only two alleles... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
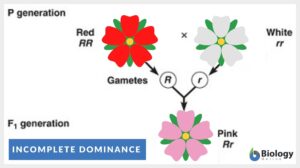
Incomplete dominance
Incomplete Dominance Definition After Gregor Mendel discovered inheritance laws, the term ''incomplete dominance'' was... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is a type of breeding or mating where closely related individuals with a common ancestor produce progenies with... Read More
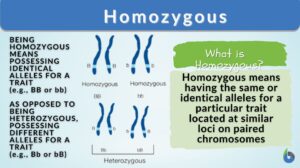
Homozygous
Homozygous Definition Diploid organisms that have a genotype of identical alleles for a trait or phenotype at a specific... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Transactivation
Definition noun, plural: transactivations (molecular biology, genetics) The stimulation of transcription by expressing an... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Imprinting
What does imprinting mean? Have you watched the TV cartoon show “Tom and Jerry” with an episode of a duck and its... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
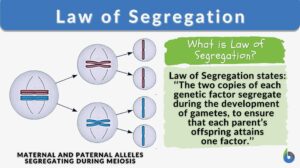
Law of Segregation
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance The father of genetics, Gregor Mendel, reported his findings in 1860 that initially were... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Glucocorticoid
Definition noun, plural: glucocorticoids Any of a group of corticosteroids involved in carbohydrate metabolism (e.g.... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Enhancer element
Enhancer element (Science: molecular biology) a dna sequence, present in the genomes of higher eukaryotes and of various... Read More
Biotic potential
When we look at the different forms of life, we often wonder how they have continued to exist one generation after another.... Read More
Sex-linked trait
Definition of Sex-Linked Traits A sex-linked trait is an observable characteristic of an organism that is influenced by the... Read More
Polygenic trait
Polygenic Trait Definition Polygenic trait refers to a trait that is controlled by multiple non-allelic genes. These genes... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More