Search Results for: fixed
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
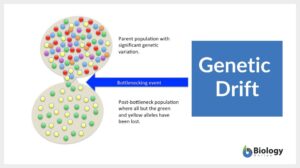
Genetic drift
Genetic Drift Definition What is genetic drift in simple terms? The simple definition of genetic drift ( also referred to... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
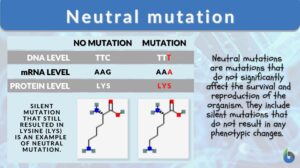
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
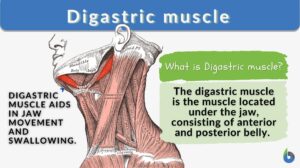
Digastric muscle
Digastric Definition The digastric muscle is a paired muscle located under the jaw, consisting of the anterior and... Read More
Genetic diversity
Genetic Diversity Definition Each species is composed of individuals with their own set of genes. A gene is the inheritance... Read More
Revolution
revolution 1. The act of revolving, or turning round on an axis or a center; the motion of a body round a fixed point or... Read More
Musculus biventer mandibulae
musculus biventer mandibulae --> digastric muscle (Science: anatomy) One of the suprahyoid group of muscles consisting of... Read More
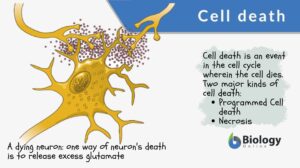
Cell death
Cell Death Definition Cell death refers to the event that leads to the death of a cell. The process entails the breaking... Read More
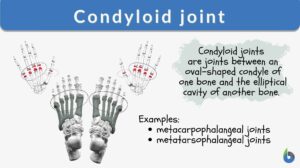
Condyloid joint
A joint is a point where two bones are attached and are capable of movement. The joints not only provide the movements of... Read More
Cell immobilization
Definition noun (biotechnology) A process wherein cells (animal or plant cells) are fixed in a suitable matrix and are used... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Prop root anatomy of Philodendron bipinnatifidum Schott (Araceae)
Prop root anatomy of Philodendron bipinnatifidum Schott (Araceae) VIANNA, Wânia de Oliveira, SOARES, Marli Kasue Misaki... Read More
Mendel’s laws: definitions
Genetics - a branch of biology that deals with the study of heredity and variations Variations - differences amongst the... Read More
Adaptation
Adaptation Definition In biology and ecology, adaptation refers to the process of adjusting behavior, physiology, or... Read More
Unconditioned stimulus
An unconditioned stimulus inherently triggers an automatic response, not reliant on deliberate prior learning. In contrast... Read More