Search Results for: h substances
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
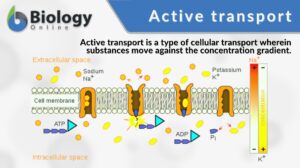
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Passive transport
Passive transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances such as ions and molecules move down their respective... Read More
Homogenous
What is homogenous? What does homogenous mean? The word homogenous has been derived from two Greek words that are... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
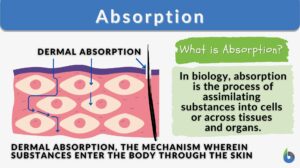
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
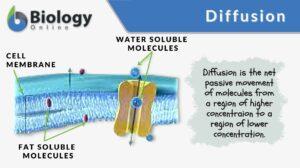
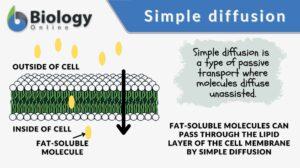
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More
H substances
h substance (Science: haematology) a polysaccharide precursor molecule which is used to make the antigens on the surface of... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More