Search Results for: homozygous
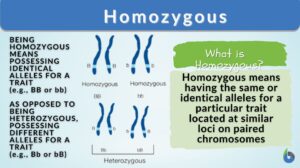
Homozygous
Homozygous Definition Diploid organisms that have a genotype of identical alleles for a trait or phenotype at a specific... Read More
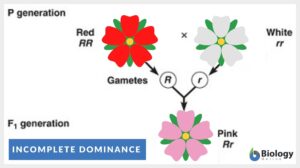
Incomplete dominance
Incomplete Dominance Definition After Gregor Mendel discovered inheritance laws, the term ''incomplete dominance'' was... Read More
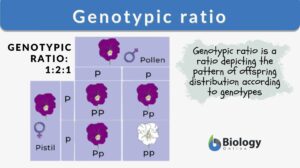
Genotypic ratio
Genotypic Ratio Definition To understand 'Genotypic ratio', let us first understand the terms: 'Genotype' and 'Phenotype'.... Read More
Codominance
Codominance Definition Codominance is a form of inheritance wherein the alleles of a gene pair in a heterozygote are fully... Read More
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is a type of breeding or mating where closely related individuals with a common ancestor produce progenies with... Read More
Allele frequency
Definition noun, plural: allele frequencies The frequency of an allele relative to that of other alleles of the same gene in... Read More
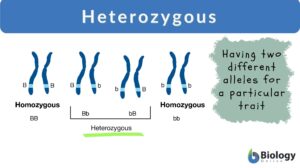
Heterozygous
Heterozygous Definition adjective (genetics) Of, or pertaining to an individual (or a condition in a cell or an organism)... Read More
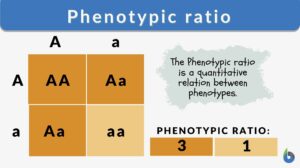
Phenotypic ratio
Phenotypic Ratio Definition How would one define phenotypic ratio? The correlation between the amount of offspring that... Read More
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. The inheritance patterns seen in Mendel's monohybrid and dihybrid crosses... Read More
Polymorphism
Polymorphism Definition The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred... Read More
Disruptive Selection
An evolutionary process known as disruptive selection (or disruptive natural selection) causes a population to become... Read More
True breeding
Definition noun A kind of breeding in which the parents with a particular phenotype produce offspring only with the same... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
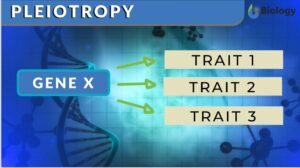
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy Definition When one single gene starts affecting multiple traits of living organisms, this phenomenon is known... Read More
Monohybrid cross
Definition noun A genetic cross between homozygous individuals but with different alleles for a single gene locus of... Read More
Heterozygote
Definition noun, plural: heterozygotes A nucleus, cell or organism possessing two different alleles for a particular... Read More
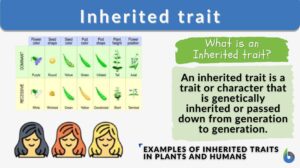
Inherited traits
What are Inherited Traits? The characteristics or traits that are passed from parents to offspring are known as inherited... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
X-linked inheritance
Definition noun (genetics) Inheritance for genes on the X chromosome Supplement Sex chromosomes are not only relevant for... Read More
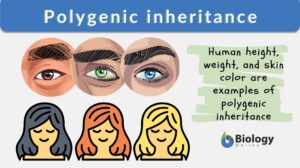
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Pseudodominance
Definition noun (genetics) The manifestation of a recessive trait, mimicking an inheritance of a dominant... Read More
Inbreeding depression
Definition noun, plural: inbreeding depressions The loss of vigour or the reduced biological fitness in a particular... Read More
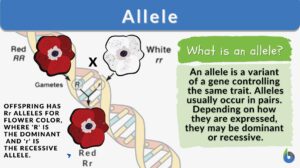
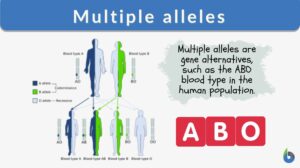
Multiple alleles
Alleles are the pairs of genes occupying a specific spot called locus on a chromosome. Typically, there are only two alleles... Read More
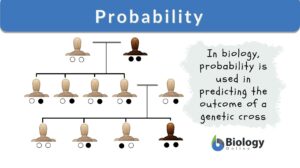
Probability
Probability Definition How do you define probability? In science, probability is a measurement tool that calculates the... Read More
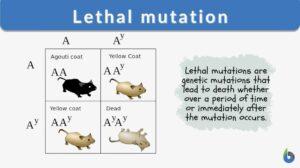
Lethal Gene
Any gene that has an effect that causes the death of the organism at any stage of life.A genes whose effect on the phenotype... Read More
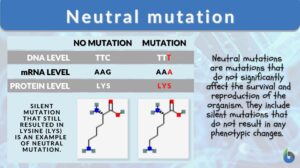
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
Test cross
Definition noun Crossing an organism with dominant genotype to a recessive homozygote for a specific phenotype in order to... Read More
Hemizygous
Definition adjective (1) Characterized by having one or more genes without allelic counterparts. (2) Pertaining to a diploid... Read More
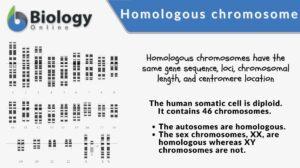
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
Lethal mutation
Lethal Mutation Definition Genetic mutations come from changes in the DNA structure or sequencing in an organism. Often... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More